Railway Safety
At KORAIL, a number of highly skilled professionals with strong work ethic and extensive experience are committed to ensuring safe rail services. Their passion for safety is the driving force behind KORAIL’s Safety First policy.
General safaty
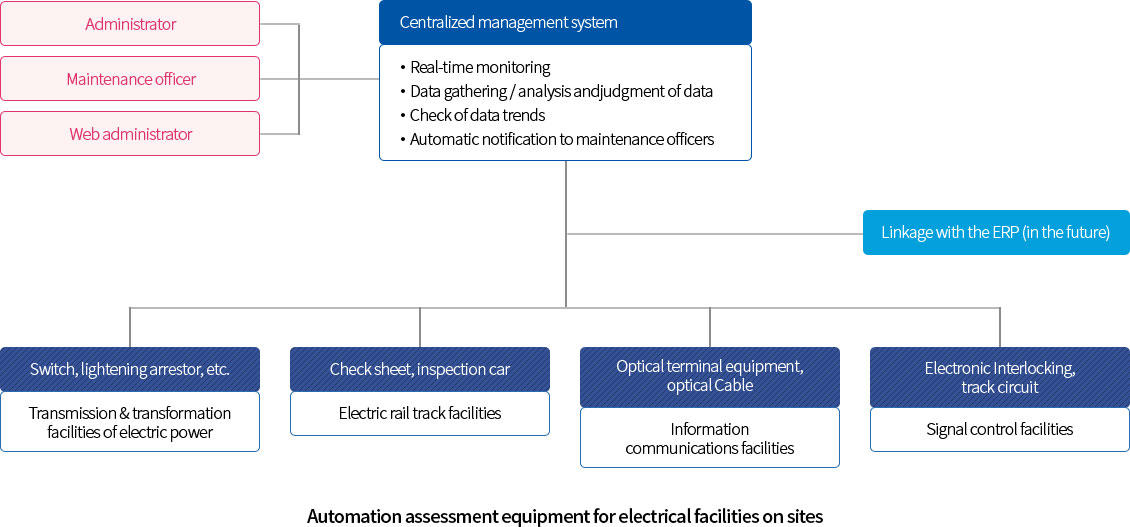
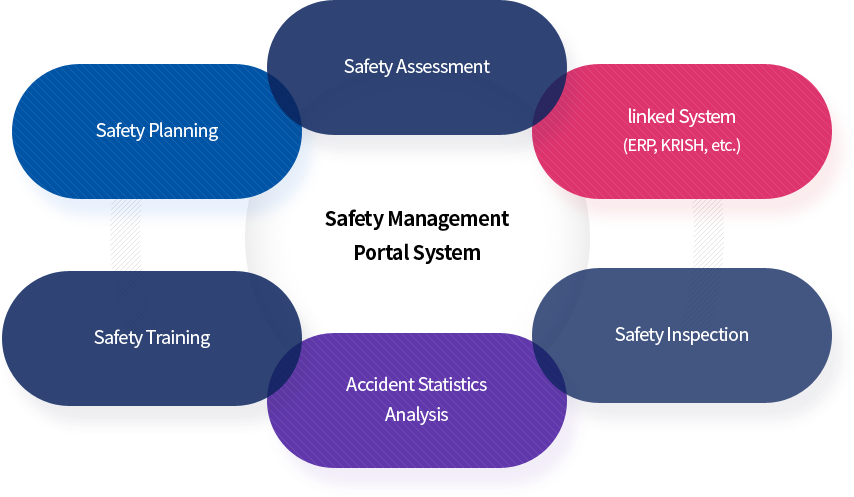
Establishment of a safety management system
- Establishment of a portal system to manage safety
- Establishment of a risk-based railway safety management system
- Operation of a program for fire prevention facilities management
- Identification and sharing of cases of risk
Establishment of a disaster response system
- Operation of KORAIL Risk Management Center
- Preparation of an emergency response manual
- Operation of a permanent disaster response center
- Operation of a real-time information receiving system in the event of earthquake
Adoption of advanced safety management techniques
Establishment of a risk analysis and assessment system
Strengthening of accident investigation and analysis processes
- Investigation and analysis of the cause of accidents and corrective action
- Identification and sharing of the cases of risks to prevent accidents
Rolling stock safety
Operation of competency building programs
Rail Safety
Running capacity strengthening program
Technical Support for Safe Train
Operation by Strengthening Technical Competences
-
Specialized training
-
Monitoring & feedback
-
Evaluation & compensation
-
Evaluation & compensation
-
Communication
- Establishment of a link with management strategies
- Establishment of cle ar go als for sophistication of the rail sector
- Sharing of objective s and thorough management of track re cord
- Strengthening of cooperation with experts
-
Sophistication of railway technologies
- Establishing quality management system
- Strengthening of the KTX-RCM system
- Decision-making system for track management
- Establishment of the on-board computer system
-
Establishment of a reliability management system
- Establishment of a reliability management system
- Strengthening of the reliability of rolling stock inspections
- Expansion of the convenient facilities for customers
-
Fostering of rail technology experts
- Training of global experts
- Cooper ation in high-speed rolling stock
- Strengthening of job competency
- Strengthening of advanced technology training
- Operation of an advanced maintenance system
- Joint research on building a mutually beneficial network of technology cooperation to secure state-of-the-art technologies
- Analysis of the cause of rolling stock failures and development of preventive measures against failures
- Intensive management of failure-prone core parts and development of preventive measures
- State-of-the-art safety equipment for high-speed rolling stock
- Equipment for monitoring the driving status of the KTX
- State-of-the-art three-fold braking device: regenerative braking, rheostatic braking, and friction braking
Facility safety
- Establishment of a 24-hour comprehensive monitoring and control system to protect main facilities
- Installment of infrared cameras with a 10x zoom in tunnels and bridges
- Installment of a fence alarm system in high-risk areas (residential and mountains areas)
- Realization of the “zero disaster” goal by establishing a scientific safety management system
- Earthquake detection and automatic rainfall alarm system
- Automatic flood-level alert system for railroad bridges
- Reinforcement of rail track section and establishment of a monitoring system
- Safety enhancement by modernizing of facility maintenance equipment
- Track inspection car, electrified track test car, track stabilization equipment car, turnout compactor, etc.
- Establishment and operation of the Disaster Response Center
- State-of-the-art safety facilities for high-speed railways
- Weather monitoring device, dragging equipment, rail temperature detector, rail-axle temperature detector, and obstacle/falling stones detector
Electrical safety
Establishment of a centralized control system for the nationwide rail networks based on an advanced rail traffic control system
Rail Traffic Control System
-
CTC
- Overall monitoring of train operation status on conventional lines
- Centralized control on trains
-
Communication Facility
- Real-time transmission of traffic control data
- Connection between the Center and sites
-
SCADA
- Remote control of power supply facilities
-
High-speed CTC
- Overall monitoring of high-speed train operation status
- Centralized control of high-speed trains
-
A remote control system based on the Automatic Train Control (ATC)
The ATC is the equipment that displays speed limits by continuously transmitting speed information necessary for safe train operation via rail and that reduces train speed reduction automatically when the speed limit is exceeded. -
Automatic Train Protection (ATP) System
The ATP system is a train operation control system where an on-board computer detects train speed and automatically reduces/controls the speed when the speed limit is exceeded. -
Moving Block System (MBS)
The MBS is a metro train operation control system that adjusts the location and speed of a train and the distance between trains by using wireless communications - A failure prediction system for electrical facilities